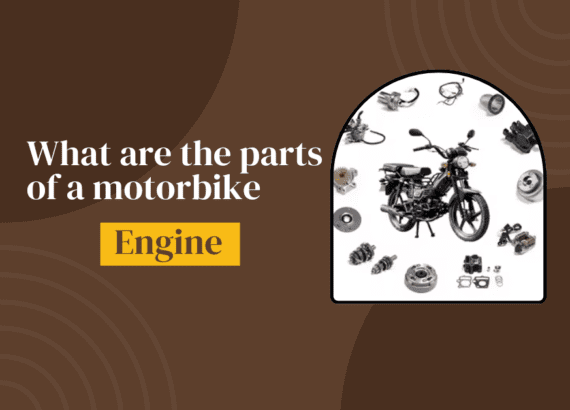
What are the parts of a motorbike engine?

Exploring the core and origin of a motorbike engine reveals much about the grandeur and sturdy design that caters to every biker’s needs. At its heart, the engine serves not just as a machine. But as the control center orchestrating every function with impeccable coordination. The bike’s engine, akin to the brain of the vehicle, takes the responsibility of ensuring smoothness and stability in the ride. Embodying the essence of what makes riding an exhilarating experience. Understanding the technicality behind its functioning offers a fascinating glimpse. How these mechanical marvels are a helping hand to riders. Guaranteeing safety and pleasure in every turn.
Diving deeper, the bike engine comprises several parts, each with its unique names and roles. Working in perfect harmony to perform various tasks. A closer look at these components helps us understand the criticality of their functions . How they are perfectly carried out regardless of the situation. Among these, the piston, crankshaft, cylinder, and camshaft stand out as trademarks of the engine’s might and efficiency.
Each part, a masterpiece of engineering, contributes to the overall functioning of the bike. Ensuring control and coordination that sets the stage for a smooth ride. This intricate internal weave of parts and their respective tasks highlight the technicality and precision that go into the making of a motorbike. As a former mechanic, I’ve spent countless hours with my hands greased. Working on these engines, marveling at the precision and innovation embedded in every component. It’s this intricate ballet of parts and functions, carried out with smoothness and stability. That reinforces the bike engine’s role as the undeniable brain of the machine. Embodying trademarks of speed and grandeur on the open road.
Engine
Exploring the heart of a motorcycle, the engine is a marvel of internal combustion engines that converts gasoline into kinetic power, thrusting the rear wheel into motion. Within this powerhouse, pistons travel within the cylinder block, orchestrated by the crankshaft to transfer energy through the gearbox.
The engine’s classification is influenced by its cylinders and cubic capacity, essential in determining the bike’s power output. Two-stroke and four-stroke engines differentiate in power strokes per revolution, affecting performance and efficiency.
My hands-on experience with these systems has deepened my understanding of how each component, from the cylinder head to the intricate dance of pistons, contributes to the motorcycle’s lifeforce, driving the rear wheel and fueling the adventurer’s spirit.
Cylinder Heads
Diving deep into the engine, the core of any vehicle’s locomotion, we find ourselves inspecting its vital parts. My personal journey through motorcycle maintenance has taught me the critical role of the cylinder heads in the internal combustion process. Where fuel—be it petrol or diesel—mixes with air to ignite and propel the bike forward.
These components, often crafted from durable iron or lightweight aluminum alloy, are crucial for sealing the combustion chamber. This sealing is paramount, keeping the combustion safe and confined. Preventing any leaks that could lead to abnormality or problems in engine performance.
The cylinder heads play a decisive role in the engine’s respiration, allowing it to “breathe” by facilitating the entry of fuel and exit of exhaust, thereby completing the cycle of propulsion. Any hiccup in this process can lead to smoke, signaling an issue that needs immediate attention. Through hands-on experience, I’ve learned that these components are not just parts; they are critically useful in ensuring the smooth operation and longevity of the bike.
Their ability to withstand extreme conditions while maintaining the integrity of the combustion process is a testament to the marvel of modern engineering in the realm of internal combustion engines.
Cylinders
At the core of the engine’s performance are the cylinders. These are not just ordinary metal tubes; they are the chambers where fuel combustion occurs, propelling the vehicle forward with energy. Made typically from cast iron or aluminum alloys to allow free movement of the pistons within a tightly sealed area. They are paramount for efficient engine operation.
Motorbikes can sport anywhere from one to six cylinders. Each configuration offering a balance between power, fuel efficiency, and how the bike is to play out in certain situations. For my own projects, I’ve found that two-cylinder engines strike a splendid balance between performance and manageability. Making them a standard use choice for those seeking a machine that’s both powerful and practical for everyday adventures.
However, it’s this intricate dance of components, each central to the engine’s ability to function properly. That underscores the beauty of motorcycle engineering. Without this harmonious interaction, the bike would be at risk of becoming dangerous to operate.
Pistons
At the core of the engine’s combustion chamber, pistons perform an oscillating movement, tirelessly moving upwards and downwards as they convert the energy generated during combustion into motion. This dance is pivotal in propelling a bike forwards. They are traditionally crafted from materials such as aluminum. Steel alloys, cast iron, and nickel to withstand extreme conditions and temperatures. However, if tragedy strikes and a piston breaks, it’s advised to abandon the vehicle immediately.
Continuing to ride could lead to deadly accidents, underscoring the important role these bike engine parts play in our safety. The connecting rods, often overlooked yet vital. Bridge the gap between pistons and the crankshaft. Transferring the upwards and downwards motions into a rotation that drives the wheels. Their reliability is paramount, and much like the pistons, they’re built from robust materials to ensure longevity.
Drawing from personal experience, I’ve seen engines torn apart and rebuilt. Each time gaining a deeper understanding of the delicate balance between power and durability. The tragic downfall of neglected engines serves as a stark reminder of the importance of regular maintenance and the decision to abandon a ride if critical parts fail.
This has not just honed my respect for the engineering behind these machines. But has deeply ingrained the necessity of knowing the name of each part and its function. Whether it’s the rhythmic dance of the pistons or the steadfast support of the connecting rods. Each component plays a crucial role in the journey, turning mere motion into miles of memories.
Connecting Rods
From my years tinkering with motorbikes, I’ve learned to appreciate the harmony within the engine. It begins with the pistons, integral parts that move up and down within the cylinder block, initiating combustion. But the true marvel of engineering lies in the connecting rods. These rods serve as critical bridges, facilitating the interconnection and ensuring seamless coordination between the pistons and the crankshaft.
It’s this linkage that converts the linear motion of the pistons into the rotation needed to drive the motorcycle’s wheels. Over time, I’ve observed manufacturers experimenting with materials like titanium and aluminum, each chosen for its strength to weight ratio, enhancing performance and durability. This exploration into materials science underscores the complexity of engine design. Where every part is pivotal to the overall machine’s efficiency and power.
Crankshaft
Venturing into the engine parts of a motorbike introduces you to a fascinating world where dynamics, kinetics, and precision engineering meet to set the stage for the movement that powers your ride. From personal experience, the layout and function of these parts can seem daunting. Yet their unique shape and operation are what make riding a bike a distinct pleasure.
Central to this system is the crankshaft, a piece revered for transforming the linear motion of pistons into rotary motion necessary for propelling the wheels. This rotation is no simple feat—it demands a complete and timing-perfect coordination between the crankshaft, connecting rods, and pistons. What’s fascinating is how this rhythmic motion is achieved; each component, from pistons to connecting rods, works in harmony to move the bike.
This intricate dance is guided by the crankshaft. Which stands out for its special demand on different principles of physics to accomplish this seamless movement. Its role underscores the reason motorbiking feels so uniquely exhilarating.
Spark Plugs
Riding through the twist and turns of rugged terrains. I’ve learned that the engine of my bike is much more than a mechanical marvel; it’s the heart, converting chemical energy into mechanical energy through a precise dance of air, fuel, and ignition. At the core of this process lies an often overlooked yet essential part: the Spark Plugs.
These replaceable components are critical in managing the temperature within the cylinders, ensuring the combustion system functions efficiently. Without a properly working spark plug. The engine would fail to transform the air and fuel mixture into the explosive power necessary to propel the bikes forward.
My experiences with maintaining my bike have taught me the importance of these parts. Not just by name but by the vital role they play in the journey from chemical to mechanical energy.
Engine Valves
In my years of tinkering and riding, prioritizing bike maintenance has taught me the significance of understanding engine components, notably the engine valves. These are crucial for regulating the passage of air and fuel into the cylinders, facilitating the combustion process. Conversely, they also oversee the expulsion of smoke and fumes post-combustion. An activity as vital as the ingestion of the air-fuel mixture.
The efficiency of an engine, to a great extent, relies on the seamless performance of these valves. Ensuring they are in check is akin to keeping a close track on the heart of your bike’s engine. As they control the very breath of its operation – the rhythmic intake and exhale that powers your ride. This intricate list of activities performed by the engine valves underlines their priority in engine maintenance and control.
Cooling System
Having spent years tweaking and tuning motorbikes, I’ve come to appreciate the intricacies of their engines. One critical component is the parts of a cooling system, designed ingeniously to dispel heat generated from burning fuel. This conversion of fuel into mechanical energy is an intense process that without a proper cooling system, would lead to engine damage as it overheats. There are primarily two types of cooling systems found in bikes:
Air Cooling System and Liquid Cooling System. The Air Cooling System relies on air flow to reduce temperature. Making it simpler but less effective in high-performance models where the heat output is significant. On the other hand, the Liquid Cooling System uses a coolant to absorb excess heat. Circulating it away from the engine to be cooled. Thus providing more consistent temperature control and minimizing the risk of overheating.
Each system has its own merits, and choosing between them often depends on the balance between cost, complexity, and cooling efficiency that best suits the rider’s needs.
Battery
Delving into the heart of any motorbike lies its engine, a masterpiece of mechanical energy conversion. My journey through motorcycle maintenance shed light on the pivotal role of the battery. An often underestimated hero in this complex ecosystem. The battery serves as the first domino in the chain of electrical energy distribution.
It kick-starts the ignition system, ensuring that chemical energy is seamlessly transformed into electrical energy necessary for firing up the engine. This stored power not only breathes life into the engine. But also supports vital functions such as illuminating headlights for a safe ride during nighttime.
Through personal experience, a well-maintained battery symbolizes the heart of the bike, pumping essential energy to all other parts, maintaining the symphony of motion and light.
Exhaust System
Delving deep into the motorbike engine’s anatomy, the Exhaust System plays a pivotal role in defining its performance and audibility. My years of riding and tinkering with bikes have taught me that proper understanding and maintenance of the exhaust system can significantly transform your riding experience. At the heart of the motorcycle lies the engine, a marvel of engineering, composed of cylinders and a combustion chamber where the magic happens – fuel mixes with air, ignites, and generates power.
But what happens to the gasses produced in this fiery dance? This is where the exhaust system springs into action, channeling gasses away from the engine through header pipes. These glasses then pass through a catalytic converter, where harmful emissions are reduced, finally exiting the bike through silencers, which reduce noise. The orchestration of these systems ensures both the bike’s performance and its environmental footprint are kept in check, proving that every component, no matter how small, plays a significant role in the symphony of motorcycle engineering.
Transmission
Diving into a motorbike’s heart, the transmission plays a crucial role, acting as the bridge between raw power and the rear wheel. Ensuring your bike moves forward with grace or backs up when needed with a reverse function, a rarity but found in some exotic touring bikes.
My years wrenching on modern motorcycles have taught me the fascinating dance of gears within the gearbox. A ballet that dictates engine speed and how effectively it translates to momentum.
While traditional bikes opt for manual control, offering a tactile connection to the machine’s pulse, automatic transmissions have gained ground. Offering a smoother ride with less input from the rider. This intricate component ensures your journey is not just about moving from point A to B but about experiencing the sheer exhilaration of riding.
Gas Tank

Embarking on a journey to understand the intricacies of a motorbike’s engine starts with one of its most recognizable components: the Gas Tank. This crucial part not only stores fuel but also plays a pivotal role in determining how far the bike can travel. Reflecting on personal excursions across varied landscapes. The size of the tank, measured in gallons, directly influences the distance one can cover without the need for refueling.
Miles per gallon stand out as a key performance indicator, varying significantly based on a slew of factors such as the engine’s cubic capacity, the environment it operates in, the type of motorcycle, its usage, and not to forget, the rider’s riding style. Mastery over these elements not only enhances the journey but also fine-tunes the machine’s harmony with its rider, making every expedition memorable.
Wheels
Straight into the wheels aspect, it’s fascinating to see how they bear the collective weight of the rider, possibly a pillion, and maybe even some luggage. The rims, either spoked on vintage motorcycles and dirt bikes or made of alloy for modern street bikes and high-performance machines. Play a crucial role in maintaining stability.
Personal experience has taught me that the choice between spoke and alloy wheels largely depends on the ride’s intended purpose and the manufacturing era of the motorcycle. Each type offers unique benefits, whether it’s the durability and classic aesthetic of spoked wheels on a vintage bike or the sleek. Efficient performance of alloy wheels on contemporary models. As a motorcycle enthusiast, understanding the interplay between these components reveals much about the engineering marvel that is a motorcycle
Tires
When embarking on the touring journey, the significance of tires cannot be overstated. Manufacturers meticulously design. Them with a blend of materials and compounds to ensure they can withstand the variations of surfaces a rider might encounter. From long-distance escapades over terrains filled with rocks and potholes to daily riding across uneven city streets. The choice of tire becomes a pivotal link to the bike’s overall performance.
I’ve personally seen the effects of wear over years, noticing how a once durable tire begins to decline in both grip and efficiency. It’s a testament to the fact that a thorough inspection for signs of wear, available, and uneven patterns is critical every few months or after any extreme riding conditions.
Riding on specific tires made for your motorcycle enhances not only the machine’s ability to clutch the road but also significantly improves safety and enjoyment. The compounds used in these tires are advanced, interwoven with technology to offer the best grip and longevity possible. Especially important when navigating through challenging surface conditions.
Manufacturers often recommend changing tires at multiple milestones throughout its life. But as someone deeply involved in the motorcycle’s ecosystem, I’ve learned the value of adapting these guidelines to real-world usage.
Variations in road conditions, riding habits, and maintenance schedules can alter those timelines drastically. Always remember, every ride depends significantly on the health of your tires; they’re not just parts of your bike, they’re your link to the road and should be treated with respect and care.
Suspension
The dynamics of a motorcycle, it becomes evident that the suspension system is a marvel of engineering designed to isolate the rider and the chassis from surface imperfections. This is achieved through a combination of springs and dampers integrated into the front forks and rear shock absorbers. The primary function of these components is to manage the sprung weight, effectively minimizing the impact of bumps and potholes.
Beyond just smoothing out the ride, a well-tuned suspension system contributes to stellar performance during cornering, acceleration, and deceleration forces by ensuring dampening is optimized to maintain proper contact with the road. From personal experience, adjusting the suspension setup to match your riding style and the bike’s weight can transform a motorcycle’s handling. Elevating both safety and enjoyment.
Brakes
Brakes on a motorcycle come in two basic types: hydraulic and cable operated. The hydraulic system uses a fluid to transfer pressure from the lever to the calipers. Which then applies force on the brake pads against the wheels to stop or slow the bike. On the other hand, the cable-operated system mechanically transfers the lever’s pressure to the brake pads. Over time, these pads wear out and require replacement to ensure the bike’s braking efficiency is not compromised. Moreover, brakes are designed to work on both the front wheel and rear with different setups such as axial mounted or radial mounted calipers. And dual calipers on some models for better load distribution and enhanced slowing capability.
Every rider knows the importance of simultaneously applying front and rear brakes to achieve a smooth stop. This practice helps maintain balance and prevents the bike from skidding, especially under harsh braking conditions. Motorcycle drum brakes, another system used in older or budget models, operate on a different principle but aim to provide the same outcome: a controlled and efficient stop.
Drawing from personal experience, understanding and respecting the intricacies of your motorcycle’s brake system, whether it be drum brakes or the more common disc brake setups with their various caliper mountings, can make a significant difference in your riding experience. It ensures not just your safety, but also the longevity of your bike, keeping both the engine and brakes in complete unison for the best performance possible.
Frame
The heart of what makes a motorcycle tick, its frame plays the pivotal role of the backbone to the entire machinery. Having spent years around these marvelous feats of engineering, I’ve observed firsthand how the frame not only bases the structural integrity of the motorcycle but also intricately houses various components essential for smooth operation.
From my experience, I’ve come to appreciate the frame’s evolution in production, transitioning from heavy steel to lighter materials like aluminum and carbon fiber, offering a perfect balance of strength and agility. It ingeniously accommodates the engine, acting as the lifeblood. While providing anchorage for the gas tank and battery, ensuring power flow throughout the bike.
Additionally, the integration of the rear suspension and steering mechanisms into the frame exemplifies the ingenious design efforts to maximize both performance and rider comfort. This structural marvel encapsulates the essence of motorcycle engineering, embodying both form and function in the pursuit of riding excellence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a motorbike engine is a complex masterpiece that powers the ride of every biker. Combining various crucial parts each playing a significant role in its operation and efficiency. From the heart of the engine, with its pistons and cylinders performing the critical combustion process. To the intricate dance of the crankshaft and connecting rods transforming that power into motion.
The cylinder heads, with their vital role in sealing the combustion chamber, and the cooling systems ensuring the engine does not overheat, reflect the engine’s sophisticated engineering. Each component, including the battery that kick-starts the engine, the spark plugs ensuring efficient combustion, and the exhaust system managing waste glasses, contributes to the machine’s overall performance. The transmission, gas tank, wheels, and tires, alongside the suspension, brakes, and the frame, integrate seamlessly to create a riding experience that is not just about mobility but a testament to human ingenuity in engineering.
Understanding these parts not only enhances appreciation for these mechanical marvels but also underscores the importance of regular maintenance for ensuring safety and longevity on the road.
FAQs
What is the engine of a bike?
Motorcycle engines are typically two-stroke or four-stroke internal combustion engines, but other engine types, such as Wankels and electric motors, have been used. A Honda Super Cub engine. The most popular motorcycle in history, with over 100 million produced.
What is the engine head in a bike?
The function of the cylinder head is to seal the top of the engine cylinders. These engine cylinders are what form the combustion chamber. It is also referred to as an engine head or the head. It is not only the combustion chamber, but shafts and valves are also found here.
What is the main part of a bike called?
The frame serves as the structural backbone of the bicycle. It connects and supports all other components. Frames can be made from various materials such as steel, aluminum, carbon fiber, or titanium and come in different shapes and sizes to accommodate different types of bicycles.
What does CC mean in engines?
The size – or cubic capacity – of a car’s engine is measured in cubic centimeters (cc). It refers to the amount of air and fuel that can be pushed through the cylinders in the engine. In most cases, the general rule of thumb is that the bigger the capacity, the more powerful it tends to be.
How many cylinders do bikes have?
While most motorcycles are powered by a single cylinder engine, they may have up to four cylinders. In India, however, single-cylinder engines are the most popular and form over 90% of the total number of motorcycles on the streets.
What is bored with a bike engine?
An engine’s bore is the diameter of each cylinder, while the stroke is the distance within the cylinder the piston travels. Basically, an engine’s maximum power depends on how many rpm it can produce