Exploring the Best Types and Functions of Crankshaft Engines

An essential part of internal combustion engines, crankshaft engines are responsible for transforming linear motion into rotating motion. They power the movement and operation of many different equipment and vehicles. Anyone interested in the field of automobile engineering, manufacturing, or who is just inquisitive about how these engines operate has to understand the many types and uses of crankshaft engines. We shall dig into the complexities of crankshaft engines in this post, looking at their varieties and the crucial jobs they do.
Basics of Crankshaft Engines

Definition and Purpose
A crankshaft engine is a mechanical component that converts the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotary motion. It accomplishes this by using the connecting rods attached to the pistons to transfer linear motion to the rotational motion of the crankshaft. The rotational motion of the crankshaft is then used to power various machinery, vehicles, and devices.
Components of a Crankshaft Engine
Typical crankshaft engines include the following essential parts:
- Crankshaft: The main component that transforms linear motion into rotational motion is the crankshaft.
- Pistons:In cylinders, pistons move up and down, producing the reciprocating motion required for an engine to run.
- Connecting Rods: Connect the pistons to the crankshaft to convert the pistons’ linear motion into the crankshaft’s rotating motion.
- Cylinders:The combustion chamber for fuel ignition is provided by the cylinders, which also house the pistons.
Types of Crankshaft Engines
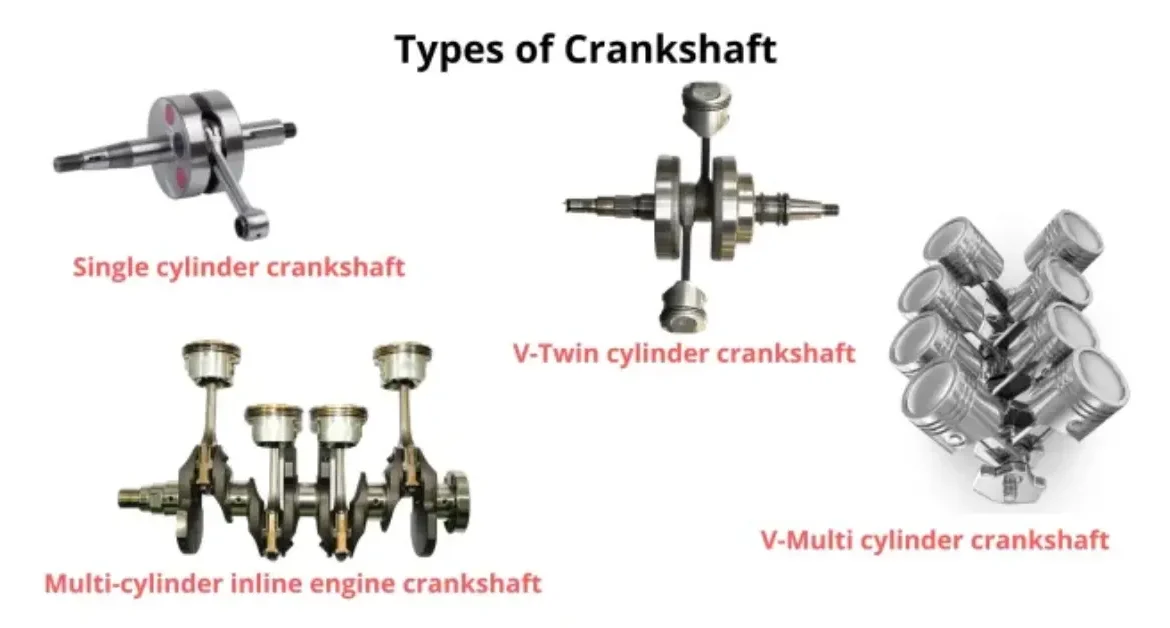
An engine’s crankshaft is a vital component that converts linear motion into rotational motion, facilitating the operation of various vehicles engines and machines. The design of a crankshaft engine plays a crucial role in determining an engine’s efficiency, power output, and overall performance. There are several types of crankshaft engines, each with its unique characteristics and applications. In this article, we will discuss the main types of crankshaft engines and their distinguishing features.
1. Inline Engine
A popular style of crankshaft engine with cylinders organized in a single straight line is the inline engine, commonly referred to as a straight engine. Because of its smooth functioning and compact construction, this combination is appropriate for a wide range of applications, including motorcycles and small- to medium-sized automobiles. Inline engines are a common option in the automobile industry since they are easy to produce and affordable.
2. V-Type Engine
The cylinder placement, which forms a V shape, gives the V-type engine its name. It is typical for the angle between the cylinder banks to range from 60 to 90 degrees. Reduced vibration and improved performance are the results of this design’s more balanced and compact engine. V-type engines are prevalent in both automotive and marine applications, especially in larger vehicles and high-performance sports cars.
3. Boxer Engine
The boxer engine, commonly referred to as a horizontally opposed engine, has opposing cylinders that are horizontally aligned. Because of this design, there is a lower center of gravity, more stability, and less vibration. Due to their distinct benefits, boxer engines are frequently found in certain cars, such as particular Subaru models and aviation engines.
4. Rotary Engine
An alternative to conventional piston engines is a rotary engine, usually known as a Wankel engine. It generates electricity by spinning a triangle rotor eccentrically inside a casing. The advantages of rotary engines are their high power-to-weight ratio, small size, and quiet operation. Due of their distinct qualities, they were frequently utilized in sports automobiles, such as Mazda’s RX-7.
5. Radial Engine
The radial engine features cylinders arranged in a circular pattern around the crankshaft. This configuration resembles the spokes of a wheel. Radial engines were widely used in aviation history, especially during World War I and II, for aircraft propulsion. They are known for their high reliability, robustness, and efficient cooling due to the radial arrangement of cylinders.
6. Opposed Piston Engine
Two pistons per cylinder in an opposed piston engine move in opposing directions. The lack of a cylinder head in this configuration makes the engine simpler and more manageable. Known for their excellent thermal efficiency, opposed piston engines have been utilized in a variety of settings, including power generators, ships, and military vehicles.
In conclusion, the kind of crankshaft engine that is selected for a particular application relies on a number of variables, including the amount of power needed, available space, operating efficiency, and intended usage. There are several variations available to meet different demands in the automotive, marine, and aviation sectors since each kind of crankshaft engine has unique benefits and is designed for certain applications.
Functions of Crankshaft Engines
Power Generation
Power production is one of the main purposes of a crankshaft engine. The connecting rods transfer the pistons’ up-and-down action to the crankshaft, which turns as a result. To power the machine or vehicle, the crankshaft’s rotational energy is captured.
Rotary Motion Conversion
Crankshaft engines are excellent at turning the pistons’ linear reciprocating action into rotational motion. In order to move forward or backward, different machines and vehicles depend on this rotating motion.
Balancing
The internal forces produced by the reciprocating action of the pistons must be balanced, and crankshaft engines are essential for this. Because of the smooth and balanced rotation that the crankshaft and its counterweights provide, vibration is reduced and engine longevity is increased.
Timing and Valve Control
The timing of the intake and exhaust valves is managed by the crankshaft via the camshaft(s). Optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and pollution control all depend on proper timing.
Advancements and Future Trends
Hybrid and Electric Technologies
There has been a noticeable trend toward hybrid and electric cars due to the increased emphasis on sustainability and environmental issues. Hybrid systems are using crankshaft engines that work in tandem with electric motors to maximize fuel economy and lower pollution.
Advanced Materials and Manufacturing
Cranking shaft components are becoming lighter, stronger, and more effective as a result of developments in materials science and production techniques. This supports improvements in the automotive and aerospace sectors by enhancing overall engine performance and efficiency.
Engine Management Systems
The performance of crankshaft engines is optimized by the advanced engine management systems included in modern engines. These systems keep an eye on a variety of characteristics and modify engine operation as necessary to increase efficiency and lessen negative environmental effects.
Conclusion
Many different pieces of equipment and vehicles depend on their crankshaft engines to operate. Understanding the many kinds and uses of crankshaft engines offers important new perspectives in the field of mechanical systems and automobile engineering. We should expect additional advancements in crankshaft engine designs as technology develops, which will result in more effective and environmentally friendly transportation options.
FAQs
Q: What is a crankshaft engine?
An engine’s crankshaft is a mechanical part that transforms the pistons’ up-and-down motion into rotating motion, which powers a variety of equipment and automobiles.
Q: What are the main components of a crankshaft engine?
The crankshaft, pistons, connecting rods, and cylinders are the essential parts, which work together to transform linear action into rotational motion.
Q: What are the common types of crankshaft engines?
There are several popular varieties, each having a unique cylinder configuration and set of uses, including single-cylinder engines, inline engines, V-type engines, and boxer engines.
Q: What is the primary function of a crankshaft engine?
Power generation, in which the engine transforms reciprocating motion into rotational motion to enable movement and industrial operation, is the main purpose.
Q: How does a crankshaft engine contribute to vehicle performance?
The power and torque required for a vehicle to run are provided by crankshaft engines, which contribute by effectively turning fuel into mechanical energy.
Q: What advancements are shaping the future of crankshaft engines?
For increased efficiency and less environmental effect, advancements include the integration of hybrid and electric technologies, the use of innovative materials, and sophisticated engine management systems.